Renv creates renv.lock file which is a JSON object and that can be a bit unweildy to handle. What if you want to find out how many packages you have? Or how many packages from installed from CRAN. What if you want to remove a package from the list? What if you want to compare lockfiles? And why not do it all from the comfort of R and tidy tools.
Read lockfile
Load the library and let’s read in a lock file. If paths are named, they are used in downstream functions else they are named automatically.
Error in get(paste0(generic, ".", class), envir = get_method_env()) :
object 'type_sum.accel' not found
# using a sample lockfile from the package
path <- file.path(system.file("extdata", package = "renvtools"), "renv-r4.4.1.lock")
# provide path to a lock file, set format to tibble
lst <- read_lock(path)
lst
R version: 4.4.1
Bioc version: 3.19
renv version: 1.0.7
Packages: 294
You can get some useful information about the lockfile. You can also explore this data as you would explore a list.
[1] "4.4.1"
[1] "3.19"
[1] "1.0.7"
[1] "1.1.4"
The default is to read into a list. Change format to tibble to read as table.
tbl <- read_lock(path, format = "tibble")
tbl
R version: 4.4.1
Bioc version: 3.19
# A tibble: 294 x 14
Package Version Source Repository Hash Requirements OS_type RemoteType
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <list> <chr> <chr>
1 BH 1.84.0-0 Reposi~ RSPM a823~ <NULL> <NA> <NA>
2 BiocManager 1.30.23 Reposi~ RSPM 47e9~ <chr [1]> <NA> <NA>
3 BiocVersion 3.19.1 Biocon~ Bioconduc~ b892~ <chr [1]> <NA> <NA>
4 CFtime 1.4.0 Reposi~ RSPM 630f~ <chr [2]> <NA> <NA>
5 DBI 1.2.3 Reposi~ RSPM 065a~ <chr [2]> <NA> <NA>
6 DiagrammeR 1.0.11 Reposi~ RSPM 584c~ <chr [19]> <NA> <NA>
7 FNN 1.1.4 Reposi~ RSPM eaab~ <chr [1]> <NA> <NA>
8 KernSmooth 2.23-24 Reposi~ CRAN 9f33~ <chr [2]> <NA> <NA>
9 Lahman 11.0-0 Reposi~ RSPM 5b6f~ <chr [2]> <NA> <NA>
10 LearnBayes 2.15.1 Reposi~ RSPM b2dd~ <NULL> <NA> <NA>
# i 284 more rows
# i 6 more variables: RemoteHost <chr>, RemoteRepo <chr>, RemoteUsername <chr>,
# RemotePkgRef <chr>, RemoteRef <chr>, RemoteSha <chr>
Note that the list and tibble formats may not be identical in information depending on the input especially in case of NAs and NULLs.
This gives you a tibble with all the package information. Now you can handle this like you would with any tibble.
# A tibble: 4 x 2
# Groups: Source [4]
Source n
<chr> <int>
1 Bioconductor 4
2 GitHub 1
3 Repository 288
4 unknown 1
# number of packages by repository
tbl |>
group_by(Repository) |>
count()
# A tibble: 4 x 2
# Groups: Repository [4]
Repository n
<chr> <int>
1 Bioconductor 3.19 4
2 CRAN 16
3 RSPM 272
4 <NA> 2
# number of packages by source and repository
tbl |>
group_by(Source, Repository) |>
count() |>
pivot_wider(names_from = Repository, values_from = n)
# A tibble: 4 x 5
# Groups: Source [4]
Source `Bioconductor 3.19` `NA` CRAN RSPM
<chr> <int> <int> <int> <int>
1 Bioconductor 4 NA NA NA
2 GitHub NA 1 NA NA
3 Repository NA NA 16 272
4 unknown NA 1 NA NA
# A tibble: 294 x 2
Package N
<chr> <int>
1 BH 0
2 BiocManager 1
3 BiocVersion 1
4 CFtime 2
5 DBI 2
6 DiagrammeR 19
7 FNN 1
8 KernSmooth 2
9 Lahman 2
10 LearnBayes 0
# i 284 more rows
Read several lock files and you get a list of tibbles or a list of lists.
paths <- list.files(file.path(system.file("extdata", package = "renvtools")), full.names = TRUE)
# read as list
# read_lock(paths[1:3], format = "list")
# read as tibble
read_lock(paths[1:3], format = "tibble")
$lf_1
R version: 3.5.3
# A tibble: 197 x 10
Package Version Source Hash RemoteType RemoteHost RemoteRepo RemoteUsername
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
1 ape 5.3 CRAN c94d~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
2 askpass 1.1 CRAN ff8e~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
3 assertt~ 0.2.1 CRAN 263e~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
4 backpor~ 1.1.3 CRAN d5d2~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
5 base64e~ 0.1-3 CRAN eec0~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
6 BH 1.69.0~ CRAN 88e6~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
7 bibtex 0.4.2 CRAN be04~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
8 bitops 1.0-6 CRAN f72d~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
9 broom 0.5.1 CRAN 3bca~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
10 callr 3.2.0 CRAN 7af0~ <NA> <NA> <NA> <NA>
# i 187 more rows
# i 2 more variables: RemoteRef <chr>, RemoteSha <chr>
$lf_2
R version: 3.6.1
# A tibble: 168 x 5
Package Version Source Repository Hash
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr>
1 BH 1.72.0-3 Repository CRAN 8f9ce74c6417d61f0782cbae5fd2b7b0
2 DBI 1.1.0 Repository CRAN 4744be45519d675af66c28478720fce5
3 DT 0.12 Repository CRAN 0e120603cc57e4f1d741f739aa8147ba
4 Formula 1.2-3 Repository CRAN 0537b6f1f38ea1fd514089192724bb6e
5 Hmisc 4.3-1 Repository CRAN b354bb2e63e1d6947eb05fa3bc355b2f
6 MASS 7.3-51.5 Repository CRAN 9efe80472b21189ebab1b74169808c26
7 Matrix 1.2-18 Repository CRAN 08588806cba69f04797dab50627428ed
8 MatrixModels 0.4-1 Repository CRAN d57ac35220b39c591388ab3a080f9cbe
9 R6 2.4.1 Repository CRAN 292b54f8f4b94669b08f94e5acce6be2
10 RColorBrewer 1.1-2 Repository CRAN e031418365a7f7a766181ab5a41a5716
# i 158 more rows
$lf_3
R version: 4.0.5
# A tibble: 424 x 6
Package Version Source Repository Hash Requirements
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <list>
1 BH 1.72.0-3 Repository CRAN 8f9ce74c6417d61f07~ <NULL>
2 BayesianTools 0.1.8 Repository CRAN 6f37f391a9029a6490~ <chr [14]>
3 Brobdingnag 1.2-6 Repository CRAN 365629a3ac7243df8e~ <NULL>
4 DBI 1.1.0 Repository CRAN 4744be45519d675af6~ <NULL>
5 DHARMa 0.4.6 Repository CRAN ffebef4763cbacec39~ <chr [6]>
6 DT 0.15 Repository CRAN 85738c69035e67ec4b~ <chr [6]>
7 Epi 2.46 Repository CRAN 8c034ee3794ad710b8~ <chr [12]>
8 FNN 1.1.3 Repository CRAN b56998fff55e4a4b48~ <NULL>
9 Formula 1.2-3 Repository CRAN 0537b6f1f38ea1fd51~ <NULL>
10 GGally 2.0.0 Repository CRAN f767c7f049252543d1~ <chr [9]>
# i 414 more rows
Write lockfile
Filter packages as needed and then write to a new lock file.
Reading a lockfile and then writing it may not give identical lockfiles as NAs and NULLs may be discarded.
# exclude bioconductor packages
tbl1 <- tbl |> filter(Source != "Bioconductor")
write_lock(tbl1, "renv-mod.lock")
Summarizing lock files
Summarize multiple lock files.
# A tibble: 8 x 8
label rver renvver pkgs_len repositories sources pkgs pkgs_req
<chr> <chr> <chr> <int> <named list> <named list> <named li> <named list>
1 lf_1 3.5.3 0.9.2 197 <df [1 x 2]> <df [2 x 2]> <chr> <named list>
2 lf_2 3.6.1 0.11.0 168 <df [1 x 2]> <df [1 x 2]> <chr> <named list>
3 lf_3 4.0.5 0.16.0 424 <df [1 x 2]> <df [1 x 2]> <chr> <named list>
4 lf_4 4.1.2 1.0.3 391 <df [3 x 2]> <df [1 x 2]> <chr> <named list>
5 lf_5 4.2.2 1.0.4 256 <df [1 x 2]> <df [3 x 2]> <chr> <named list>
6 lf_6 4.3.2 1.0.3 668 <df [3 x 2]> <df [3 x 2]> <chr> <named list>
7 lf_7 4.4.1 1.0.7 294 <df [3 x 2]> <df [4 x 2]> <chr> <named list>
8 lf_8 <NA> <NA> 16 <df [2 x 2]> <df [1 x 2]> <chr [16]> <named list>
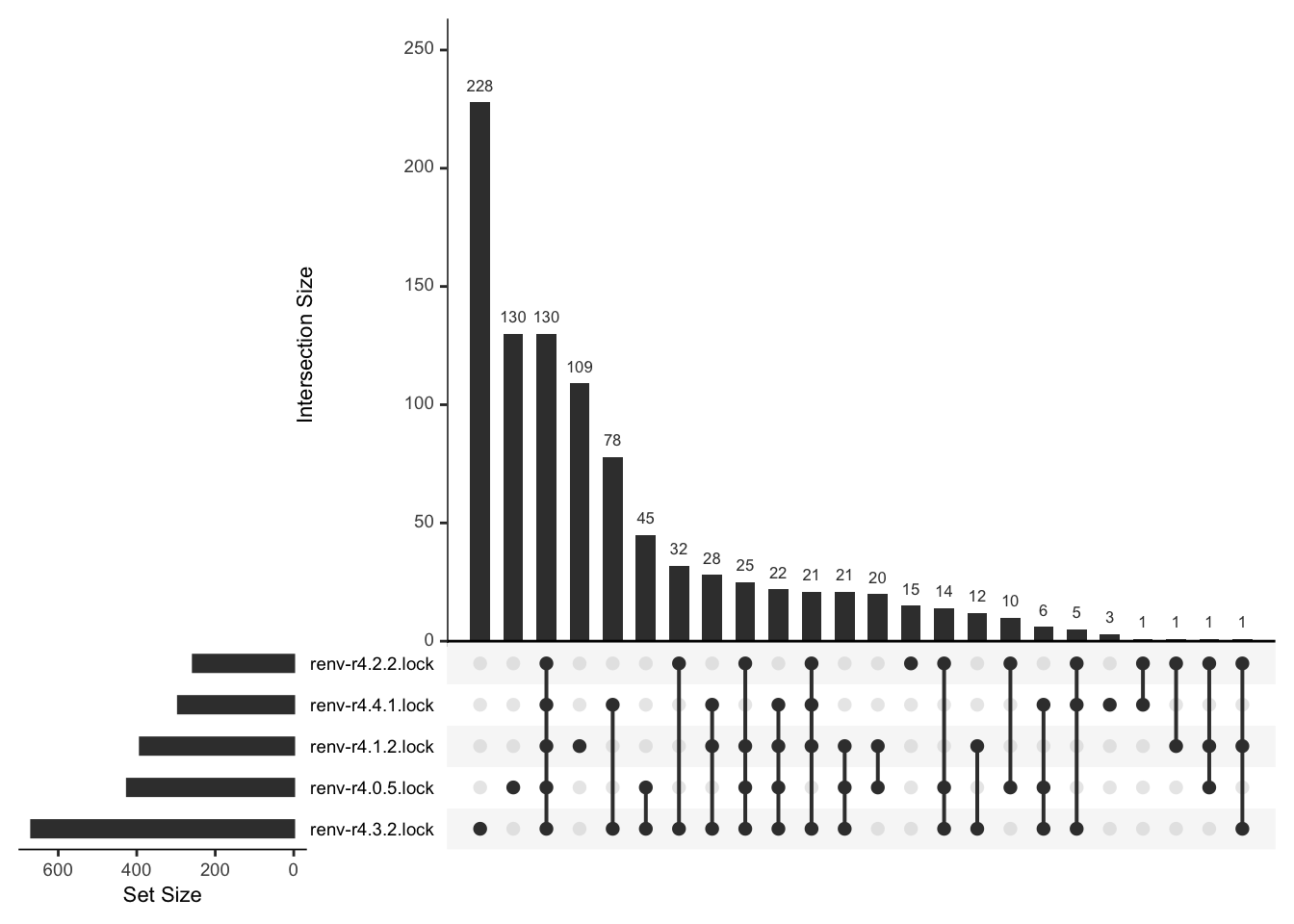
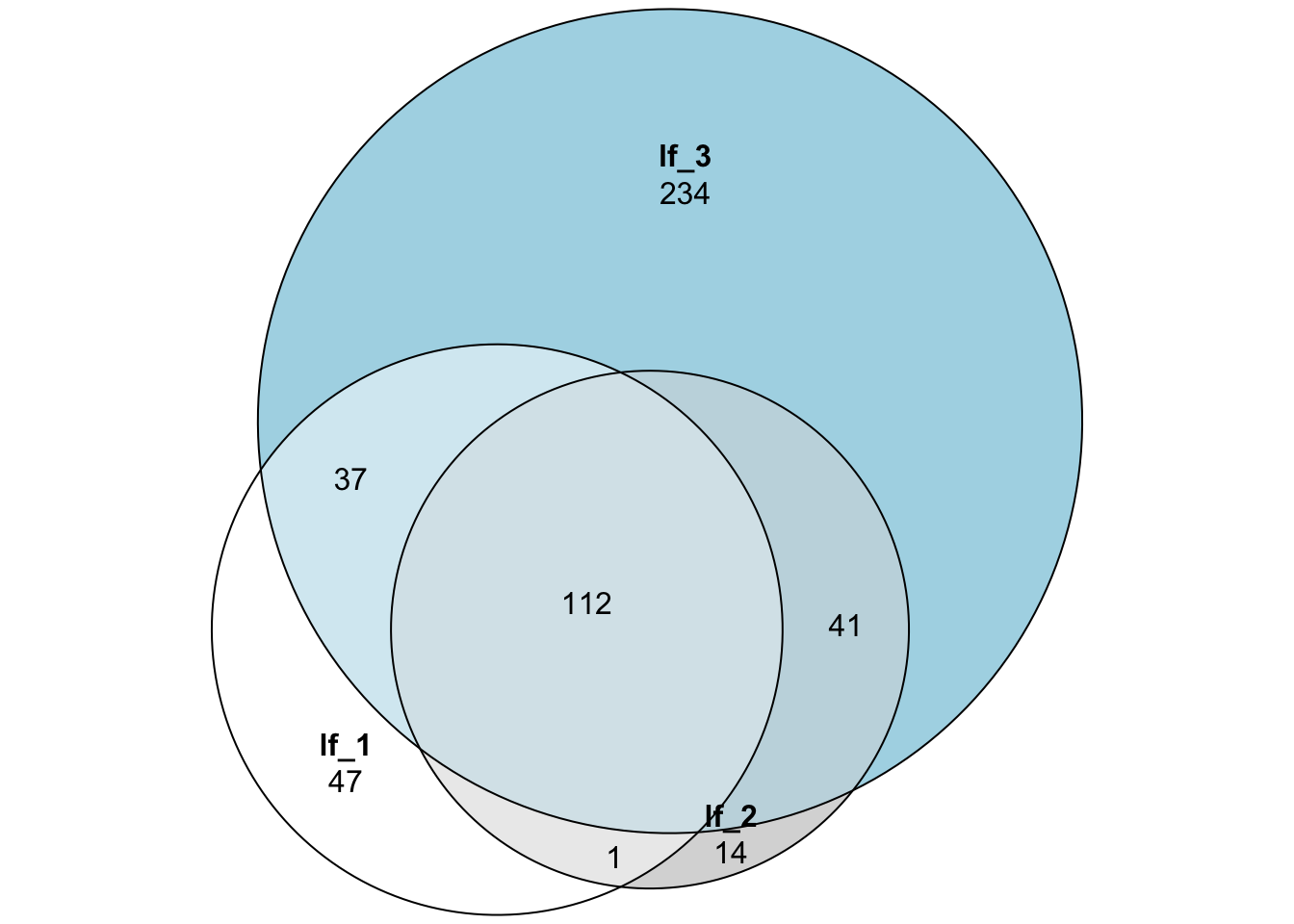
For example, visualize the difference in number of packages between lockfiles. Note that this step requires additional packages.
Comparing lockfiles
Compare two or more lockfiles in a pairwise manner.
# A tibble: 28 x 19
a b rver_a rver_b renvver_a renvver_b jaccard pkgs_len_a pkgs_len_b
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 lf_1 lf_2 3.5.3 3.6.1 0.9.2 0.11.0 0.448 197 168
2 lf_1 lf_3 3.5.3 4.0.5 0.9.2 0.16.0 0.316 197 424
3 lf_1 lf_4 3.5.3 4.1.2 0.9.2 1.0.3 0.292 197 391
4 lf_1 lf_5 3.5.3 4.2.2 0.9.2 1.0.4 0.373 197 256
5 lf_1 lf_6 3.5.3 4.3.2 0.9.2 1.0.3 0.257 197 668
6 lf_1 lf_7 3.5.3 4.4.1 0.9.2 1.0.7 0.292 197 294
7 lf_1 lf_8 3.5.3 <NA> 0.9.2 <NA> 0.0340 197 16
8 lf_2 lf_3 3.6.1 4.0.5 0.11.0 0.16.0 0.349 168 424
9 lf_2 lf_4 3.6.1 4.1.2 0.11.0 1.0.3 0.354 168 391
10 lf_2 lf_5 3.6.1 4.2.2 0.11.0 1.0.4 0.457 168 256
# i 18 more rows
# i 10 more variables: pkgs_len_unique_a <int>, pkgs_len_unique_b <int>,
# pkgs_len_common <int>, pkgs_len_total <int>, pkgs_a <list>, pkgs_b <list>,
# pkgs_unique_a <list>, pkgs_unique_b <list>, pkgs_common <list>,
# pkgs_total <list>
a b rver_a rver_b renvver_a renvver_b jaccard pkgs_len_a pkgs_len_b
1 lf_1 lf_2 3.5.3 3.6.1 0.9.2 0.11.0 0.44841270 197 168
2 lf_1 lf_3 3.5.3 4.0.5 0.9.2 0.16.0 0.31567797 197 424
3 lf_1 lf_4 3.5.3 4.1.2 0.9.2 1.0.3 0.29230769 197 391
4 lf_1 lf_5 3.5.3 4.2.2 0.9.2 1.0.4 0.37272727 197 256
5 lf_1 lf_6 3.5.3 4.3.2 0.9.2 1.0.3 0.25726744 197 668
6 lf_1 lf_7 3.5.3 4.4.1 0.9.2 1.0.7 0.29210526 197 294
7 lf_1 lf_8 3.5.3 <NA> 0.9.2 <NA> 0.03398058 197 16
8 lf_2 lf_3 3.6.1 4.0.5 0.11.0 0.16.0 0.34851936 168 424
9 lf_2 lf_4 3.6.1 4.1.2 0.11.0 1.0.3 0.35351090 168 391
10 lf_2 lf_5 3.6.1 4.2.2 0.11.0 1.0.4 0.45704467 168 256
11 lf_2 lf_6 3.6.1 4.3.2 0.11.0 1.0.3 0.22760646 168 668
12 lf_2 lf_7 3.6.1 4.4.1 0.11.0 1.0.7 0.35882353 168 294
13 lf_2 lf_8 3.6.1 <NA> 0.11.0 <NA> 0.03954802 168 16
14 lf_3 lf_4 4.0.5 4.1.2 0.16.0 1.0.3 0.36744966 424 391
15 lf_3 lf_5 4.0.5 4.2.2 0.16.0 1.0.4 0.36000000 424 256
16 lf_3 lf_6 4.0.5 4.3.2 0.16.0 1.0.3 0.31724970 424 668
17 lf_3 lf_7 4.0.5 4.4.1 0.16.0 1.0.7 0.28214286 424 294
18 lf_3 lf_8 4.0.5 <NA> 0.16.0 <NA> 0.02088167 424 16
19 lf_4 lf_5 4.1.2 4.2.2 1.0.3 1.0.4 0.38247863 391 256
20 lf_4 lf_6 4.1.2 4.3.2 1.0.3 1.0.3 0.32540676 391 668
21 lf_4 lf_7 4.1.2 4.4.1 1.0.3 1.0.7 0.41528926 391 294
22 lf_4 lf_8 4.1.2 <NA> 1.0.3 <NA> 0.03037975 391 16
23 lf_5 lf_6 4.2.2 4.3.2 1.0.4 1.0.3 0.32758621 256 668
24 lf_5 lf_7 4.2.2 4.4.1 1.0.4 1.0.7 0.39949109 256 294
25 lf_5 lf_8 4.2.2 <NA> 1.0.4 <NA> 0.03422053 256 16
26 lf_6 lf_7 4.3.2 4.4.1 1.0.3 1.0.7 0.43154762 668 294
27 lf_6 lf_8 4.3.2 <NA> 1.0.3 <NA> 0.02395210 668 16
28 lf_7 lf_8 4.4.1 <NA> 1.0.7 <NA> 0.05442177 294 16
pkgs_len_unique_a pkgs_len_unique_b pkgs_len_common pkgs_len_total
1 84 55 113 252
2 48 275 149 472
3 64 258 133 455
4 74 133 123 330
5 20 491 177 688
6 86 183 111 380
7 190 9 7 206
8 15 271 153 439
9 22 245 146 413
10 35 123 133 291
11 13 513 155 681
12 46 172 122 340
13 161 9 7 177
14 205 172 219 596
15 244 76 180 500
16 161 405 263 829
17 266 136 158 560
18 415 7 9 431
19 212 77 179 468
20 131 408 260 799
21 190 93 201 484
22 379 4 12 395
23 28 440 228 696
24 99 137 157 393
25 247 7 9 263
26 378 4 290 672
27 652 0 16 668
28 278 0 16 294
Other details
The lists are a class of it’s own called rt_list. This is why they are printed a bit differently. But, they can be treated like regular lists.
R version: 4.4.1
Bioc version: 3.19
renv version: 1.0.7
Packages: 294
The tibbles are also a class of it’s own called rt_tibble.
R version: 4.4.1
Bioc version: 3.19
# A tibble: 294 x 14
Package Version Source Repository Hash Requirements OS_type RemoteType
<chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <chr> <list> <chr> <chr>
1 BH 1.84.0-0 Reposi~ RSPM a823~ <NULL> <NA> <NA>
2 BiocManager 1.30.23 Reposi~ RSPM 47e9~ <chr [1]> <NA> <NA>
3 BiocVersion 3.19.1 Biocon~ Bioconduc~ b892~ <chr [1]> <NA> <NA>
4 CFtime 1.4.0 Reposi~ RSPM 630f~ <chr [2]> <NA> <NA>
5 DBI 1.2.3 Reposi~ RSPM 065a~ <chr [2]> <NA> <NA>
6 DiagrammeR 1.0.11 Reposi~ RSPM 584c~ <chr [19]> <NA> <NA>
7 FNN 1.1.4 Reposi~ RSPM eaab~ <chr [1]> <NA> <NA>
8 KernSmooth 2.23-24 Reposi~ CRAN 9f33~ <chr [2]> <NA> <NA>
9 Lahman 11.0-0 Reposi~ RSPM 5b6f~ <chr [2]> <NA> <NA>
10 LearnBayes 2.15.1 Reposi~ RSPM b2dd~ <NULL> <NA> <NA>
# i 284 more rows
# i 6 more variables: RemoteHost <chr>, RemoteRepo <chr>, RemoteUsername <chr>,
# RemotePkgRef <chr>, RemoteRef <chr>, RemoteSha <chr>
[1] "rt_tibble" "tbl_df" "tbl" "data.frame"
The rt_tibble objects contains only information about the packages. What about other metadata such as R version, Bioconductor version etc? These are stored as attributes along with the tibble. They are used when writing lock files. They can be accessed using attr().
$R
$R$Version
[1] "4.4.1"
$R$Repositories
Name URL
1 CRAN https://p3m.dev/cran/latest
$Bioconductor
$Bioconductor$Version
[1] "3.19"
Or from a list of renvtools tibbles.
$lf_1
$lf_1$renv
$lf_1$renv$Version
[1] "0.9.2"
$lf_1$R
$lf_1$R$Version
[1] "3.5.3"
$lf_1$R$Repositories
Name URL
1 NA https://cran.rstudio.com/
$lf_2
$lf_2$R
$lf_2$R$Version
[1] "3.6.1"
$lf_2$R$Repositories
Name URL
1 CRAN https://cran.rstudio.com
$lf_3
$lf_3$R
$lf_3$R$Version
[1] "4.0.5"
$lf_3$R$Repositories
Name URL
1 CRAN https://cloud.r-project.org
$lf_4
$lf_4$R
$lf_4$R$Version
[1] "4.1.2"
$lf_4$R$Repositories
Name URL
1 CRAN https://cran.rstudio.com
2 pik https://rse.pik-potsdam.de/r/packages
$lf_5
$lf_5$R
$lf_5$R$Version
[1] "4.2.2"
$lf_5$R$Repositories
Name URL
1 BioCsoft https://bioconductor.org/packages/3.16/bioc
2 BioCann https://bioconductor.org/packages/3.16/data/annotation
3 BioCexp https://bioconductor.org/packages/3.16/data/experiment
4 BioCworkflows https://bioconductor.org/packages/3.16/workflows
5 BioCbooks https://bioconductor.org/packages/3.16/books
6 CRAN https://cran.rstudio.com
$lf_5$Bioconductor
$lf_5$Bioconductor$Version
[1] "3.16"
$lf_6
$lf_6$R
$lf_6$R$Version
[1] "4.3.2"
$lf_6$R$Repositories
Name URL
1 CRAN https://p3m.dev/cran/latest
$lf_6$Bioconductor
$lf_6$Bioconductor$Version
[1] "3.18"
$lf_7
$lf_7$R
$lf_7$R$Version
[1] "4.4.1"
$lf_7$R$Repositories
Name URL
1 CRAN https://p3m.dev/cran/latest
$lf_7$Bioconductor
$lf_7$Bioconductor$Version
[1] "3.19"
$lf_8
named list()
Session
R version 4.4.1 (2024-06-14)
Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin13.4.0
Running under: macOS Big Sur ... 10.16
Matrix products: default
BLAS: /System/Library/Frameworks/Accelerate.framework/Versions/A/Frameworks/vecLib.framework/Versions/A/libBLAS.dylib
LAPACK: /opt/homebrew/Caskroom/miniforge/base/envs/r-4.4/lib/liblapack-netlib.3.9.0.dylib
locale:
[1] C
time zone: Europe/Stockholm
tzcode source: internal
attached base packages:
[1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
other attached packages:
[1] UpSetR_1.4.0 eulerr_7.0.2 tidyr_1.3.1
[4] dplyr_1.1.4 renvtools_0.0.0.9002
loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
[1] gtable_0.3.6 jsonlite_1.8.9 compiler_4.4.1 renv_1.0.11
[5] tidyselect_1.2.1 Rcpp_1.0.13-1 gridExtra_2.3 scales_1.3.0
[9] yaml_2.3.10 fastmap_1.2.0 ggplot2_3.5.1 R6_2.5.1
[13] plyr_1.8.9 labeling_0.4.3 generics_0.1.3 knitr_1.49
[17] polyclip_1.10-7 tibble_3.2.1 munsell_0.5.1 pillar_1.10.0
[21] polylabelr_0.3.0 rlang_1.1.4 utf8_1.2.4 xfun_0.49
[25] cli_3.6.3 withr_3.0.2 magrittr_2.0.3 digest_0.6.37
[29] grid_4.4.1 lifecycle_1.0.4 vctrs_0.6.5 evaluate_1.0.1
[33] glue_1.8.0 farver_2.1.2 colorspace_2.1-1 rmarkdown_2.29
[37] purrr_1.0.2 tools_4.4.1 pkgconfig_2.0.3 htmltools_0.5.8.1